One of the most favoured occupations for migration to Australia is nursing. It is the pathway to Permanent Residency. If you are looking to live and work as a registered nurse in Australia, this blog will run you through the most important things you need to know before setting off.
An Overview of Registered Nurses in Australia
Australia is a country which has a high demand for nurses. However, migrating to Australia as a registered nurse is a complex process, though many have successfully accomplished it. Yet another fact you have to keep in mind is that you will have to compete with highly skilled nursing professionals from around the world to move as a registered nurse in Australia.
Roles & Responsibilities of Registered Nurses in Australia
Registered nurses in Australia are trained to assess, plan, implement, and evaluate patient care. Their duties include administering medication, managing patient records, performing diagnostic tests, and educating patients and their families on health management. They work in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, private practices, community health services, aged care facilities, schools, and more. Specialised RNs might also work in areas like critical care, mental health, midwifery, or rural and remote healthcare.
In Australia, RNs carry a wide range of responsibilities:
- Providing direct patient care
- Managing and documenting medical records
- Administering medication and treatments
- Assisting in surgery and specialised medical procedures
- Educating patients and their families on health management and preventive care
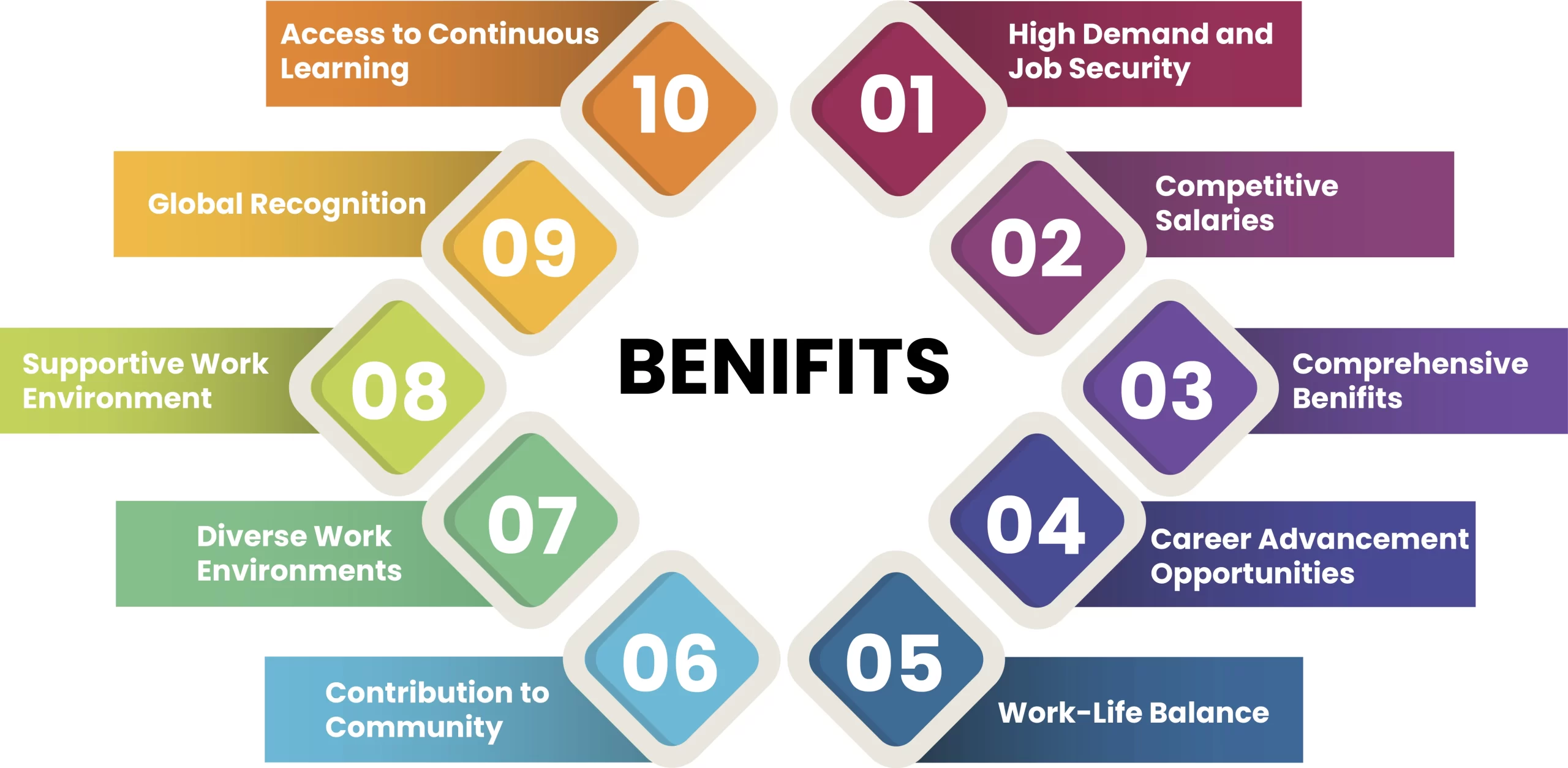
Benefits of Becoming a Registered Nurse in Australia
Migrating to Australia as a nurse offers numerous professional and personal advantages:
Competitive Salaries: Registered nurses in Australia earn between AUD 65,000 and AUD 90,000 annually, with opportunities for higher salaries in specialised roles.
Job Security and High Demand: Australia’s growing population creates a continuous demand for qualified registered nurses, ensuring a stable and secure career path.
Flexible Working Hours: Nurses in Australia typically work an average of 33 hours per week, providing a balanced lifestyle.
Diverse Employment Opportunities: The healthcare sector in Australia offers a wide range of roles across various settings.
Additional Compensation for Holiday Work: Nurses receive extra pay for working on public holidays.
Quality Lifestyle: With a high quality of life, a respected public healthcare system, and strong work-life balance, Australia stands out as an attractive destination for healthcare professionals.
Requirements to Work as a Nurse in Australia from India
To practise as an RN in Australia, overseas nurses must meet specific registration and skill requirements:
1. Educational Qualifications
Degree: A Bachelor of Nursing (or equivalent) from a recognized institution is typically required.
Coursework and Clinical Practice: Programs should include both theoretical coursework and clinical practice hours.
2. English Language Proficiency
IELTS Academic: A minimum score of 7 in each band (Reading, Writing, Listening, and Speaking).
Other Accepted Tests: The OET, TOEFL, and PTE are also accepted with specific scores.
3. Registration with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)
Application: Nurses must apply to AHPRA to verify their qualifications and experience.
Background Checks: Criminal record checks are required, along with a thorough review of the nurse’s credentials.
4. Nursing Registration Examinations
Outcome-Based Assessment (OBA): Required for internationally qualified nurses, the OBA includes:
NCLEX-RN: A written exam similar to the U.S. NCLEX for nursing knowledge.
OSCE: An Objective Structured Clinical Examination to assess clinical skills.
5. Bridging Program (if required)
Some international nurses may need to complete an AHPRA-approved bridging or adaptation program before practising in Australia.
6. Visa and Work Rights
Temporary Skill Shortage (TSS) Visa (Subclass 482): Commonly used for skilled workers, allowing temporary residence.
Permanent Residency: Skilled Migration visas, such as the Skilled Independent Visa (Subclass 189) or Skilled Nominated Visa (Subclass 190), are also options for eligible nurses.
7. Professional Experience
Work Experience: While not mandatory, experience in specialised fields (ICU, ER, etc.) can enhance career opportunities and may improve chances of gaining visas or higher-level roles.
These requirements make sure that nurses in Australia are well-qualified, and meeting them provides nurses access to a rewarding career in a high-demand field.
Age Limit for Nurses in Australia
In Australia, individuals can embark on a nursing career at any age, as there is no official age restriction for practicing nurses. However, age considerations come into play for nurses seeking migration, varying by visa category. Permanent skilled visas, such as the Skilled Independent Visa (Subclass 189) and the Skilled Nominated Visa (Subclass 190), generally impose an age limit of 45 years. Notably, a significant portion of Australia’s nursing workforce is aged 50 or older, underscoring the profession’s inclusivity and the value placed on experience. Therefore, while certain migration pathways are influenced by age, numerous opportunities exist for nurses of all ages to contribute meaningfully to Australia’s healthcare system.
Nursing Jobs in Australia for Indian Nurses
Indian nurses considering a move to Australia have many career options, with demand across various specialisations, including aged care, emergency nursing, and mental health. Skilled nurses in high-demand areas may find smoother visa processes and job opportunities, especially in rural and remote areas where healthcare workers are scarce.
Types of Nursing Jobs Available
Registered Nurse (RN): The most common role, with opportunities in hospitals, aged care facilities, and clinics.
Enrolled Nurse (EN): Works under the supervision of an RN, with slightly fewer responsibilities but still valuable in hospitals and long-term care.
Specialised Nursing Roles: Areas like critical care, emergency, paediatrics, and mental health are in high demand, often requiring specific training and experience.
Aged Care Nurse: With Australia’s ageing population, there’s a growing need for nurses in aged care facilities, home care, and palliative care.
Popular Cities for Nursing Jobs
Sydney, New South Wales: High demand for nurses but also competitive. Offers great city amenities and higher salaries.
Melbourne, Victoria: Known for excellent healthcare facilities and a high quality of life.
Brisbane, Queensland: Growing demand in hospitals and aged care, with a warmer climate and lower cost of living compared to Sydney.
Perth, Western Australia: Attractive for those seeking job opportunities outside the major east coast cities, with a lower cost of living.
Regional Areas: The Australian government offers incentives for healthcare workers in rural and regional areas, including faster visa processing and potential financial benefits.
Registered Nurse Salary in Australia
RNs in Australia earn competitive salaries that vary by experience, location, and specialisation. Here’s a rough overview of the typical salary range:
| Roles / Experience |
Annual Salary Range |
| Entry-Level RNs |
AUD 65,000 – AUD 75,000 |
| Experienced RNs or Specialists |
AUD 80,000 – AUD 100,000+ |
| Nurse Practitioners |
AUD 100,000 – AUD 120,000 |
Specialisation-Based Salaries
Critical Care/Emergency Nurses: AUD 80,000 to AUD 95,000, as these roles require specialised skills.
Aged Care Nurses: AUD 65,000 to AUD 75,000, with additional perks or allowances.
Mental Health Nurses: AUD 75,000 to AUD 90,000, depending on experience.
Operating Theatre Nurses: AUD 80,000 to AUD 100,000, as they often work with complex surgical procedures.
Additional Allowances
Shift Work: Nurses working night, weekend, or holiday shifts earn an additional 15-30% shift loading on top of their standard pay.
Overtime: Paid at 1.5 to 2 times the regular hourly rate.
Professional Development: Many employers offer paid or subsidised training, adding value to the compensation package.
Registered nurses in Australia benefit from structured pay scales, especially in public hospitals, which increase with years of service and additional certifications.
How to Migrate to Australia as a Nurse from India
Check Eligibility – Determine which visa suits you, such as Skilled Independent (189) or Skilled Nominated (190).
Meet Qualification Standards – Ensure your nursing qualifications meet AHPRA/ANMAC requirements.
Register with AHPRA – Complete the nursing registration process.
Skills Assessment – Apply through ANMAC.
Submit your Expression of Interest – Submit through Skill Select to receive an invitation to apply for visa.
Apply Online – Submit your visa application through the government portal.
Medical Examination – Complete a health check as required.
Wait for Processing – The Department of Home Affairs will review your application.
How to Become a Registered Nurse in Australia from India
Indian RNs must go through several steps to meet Australia’s registration requirements:
Educational Qualification and Equivalency: Verify that your nursing qualifications meet AHPRA standards. You may need to complete additional coursework if there are gaps.
English Proficiency Test: Pass an English proficiency test (IELTS or OET).
Outcomes-Based Assessment (OBA): Complete the OBA, an assessment for overseas nurses whose qualifications don’t automatically meet Australia’s registration standards.
Complete Clinical Placement: In some cases, Indian RNs may be required to undergo a supervised clinical placement.
Indian Registered Nurses (RNs) who aspire to work in Australia must meet several requirements to gain registration with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA). The process begins with Educational Qualification and Equivalency, where nurses must verify that their qualifications align with AHPRA standards. If there are gaps, additional coursework may be required to meet Australian nursing education criteria.
Next, candidates must demonstrate their English proficiency by taking an approved test, such as IELTS or OET, to ensure effective communication in clinical settings. A score of 7.0 in each band for IELTS or a grade “B” in OET is typically needed.
For nurses whose qualifications don’t automatically meet Australia’s standards, an Outcomes-Based Assessment (OBA) is essential. The OBA is a two-part assessment that includes a theoretical multiple-choice examination and a practical Objective Structured Clinical Exam (OSCE). This ensures that candidates possess the necessary knowledge and skills for safe practice. In certain cases, Indian RNs may also be required to undergo a Clinical Placement within an Australian healthcare facility.
These steps help Indian nurses align with Australian nursing standards, providing a pathway to a rewarding nursing career in Australia while ensuring quality care for patients.
Wrap Up
Migrating as a registered nurse in Australia opens doors to a fulfilling career in a well-regarded healthcare system, offering job security, a great quality of life, and professional growth. Whether you’re a Canadian nurse looking to move or an Indian nurse seeking new opportunities, understanding the registration requirements, job market, and benefits can make your transition to Australia smoother.
For more details about Australian immigration connect with our Australia immigration consultants ! Book a consultation today!!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Migrate to Australia as a Nurse?
- Register with AHPRA.
- Complete the Outcomes-Based Assessment (OBA) if required.
- Apply for a visa (e.g., Skilled Visa 189, 190, or Employer-Sponsored 482).
How to Get a Nursing Job in Australia from India?
- Finish AHPRA registration.
- Apply on job platforms like Seek or use Australian recruitment agencies.
- Network with other nurses to find job leads.
What is the Salary of Registered Nurses in Australia?
- Average salary: AUD 65,000 to AUD 85,000 per year.
- Hourly rate: AUD 30 to AUD 50, with extra for night/weekend shifts.
What is the age Limit for Nurses in Australia?
- Permanent skilled visas: Age limit is generally 45.
- Temporary visas (e.g., 482) may not have strict age limits, depending on employer support.
Can Nurses Work in Australia on a Temporary Basis?
Yes, the Temporary Skill Shortage Visa (Subclass 482) allows nurses to work temporarily, often with pathways to permanent residency if sponsored by an employer.
Is Work Experience Required to Work as a Nurse in Australia?
While not mandatory, at least 1-2 years of work experience is highly beneficial. Some employers prefer experienced nurses, especially for specialised roles.