Ever wondered what happens when multiple candidates have the exact same CRS score in Express Entry? Who gets the Invitation to Apply (ITA) and who has to wait? Is there anything as a tie breaking rule in Express Entry?
Imagine finishing a race at the same time as someone else, but only one person wins. That’s when Canada’s tie breaking rule in Express Entry works. It decides who gets the chance to move forward when candidates have the same CRS score
In this blog, we break down why this rule exists, how it works, and what you can do to stay ahead in the pool. Let’s untangle the tie and get you one step closer to your ITA.
Table Of Content
1What is the Meaning of Tie Breaking Rule in Express Entry2Why is the Tie Breaking Rule Important3How does the Tie Breaking Rule Work in Express Entry4Real-Life Example of Tie-Breaking Rule in Express Entry5How to Increase Your CRS Score & Avoid the Tie-Breaking Rule in Express Entry6Wrap up7Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Meaning of Tie Breaking Rule in Express Entry
The tie breaking rule in Canada’s Express Entry system is a key tool used to fairly select candidates when several applicants have the same CRS (Comprehensive Ranking System) score. This mechanism helps maintain transparency and fairness in the selection process, which is central to Canada’s skilled immigration program.
When Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) conducts an Express Entry draw, and multiple candidates share the same CRS score, the tie-breaking rule comes into play. In such cases, priority is given to those who submitted their profiles to the pool earlier, based on the date and time of submission recorded in the system.
Why is the Tie Breaking Rule Important
To ensure fairness in any competition, there’s a tie-breaking rule and the Express Entry system is no different. When multiple candidates achieve the same Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) score, the tie-breaking rule in Canada comes into play to determine who will receive an invitation to apply for permanent residence. This rule ensures that the process remains fair, transparent, and consistent, preventing any confusion or bias in selecting candidates with identical scores.
The tie breaking rule in Express Entry works by ranking candidates based on factors such as the date and time their profiles were submitted. This provides a clear, objective method for resolving ties, making sure that those who entered the pool earlier are given priority. By establishing a straightforward tie-breaking mechanism, the system ensures that every applicant has an equal opportunity, based on their CRS score and submission time, fostering trust and credibility in the immigration process.
How does the Tie Breaking Rule Work in Express Entry
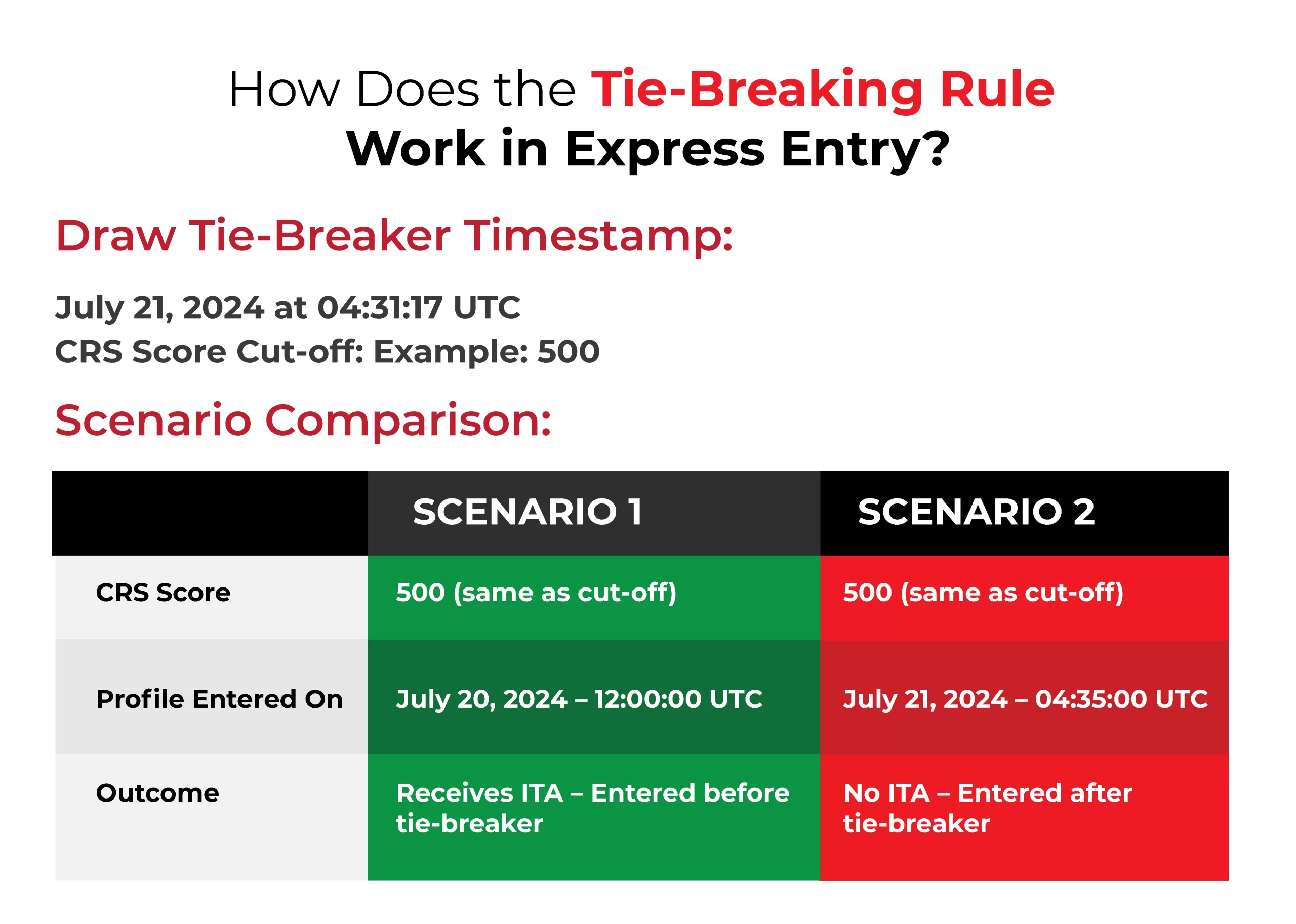
When Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) holds an Express Entry draw, it sets a minimum CRS score to filter eligible candidates. But what happens when hundreds of people share that exact score? That’s where the tie-breaking rule steps in.
To ensure fairness, IRCC doesn’t just rely on scores, it also looks at when you submitted your profile. If the cutoff score is 500 and multiple candidates are tied, the system gives priority to those who entered the pool earlier, based on the precise date and time they submitted their application.
This tie-breaking timestamp is officially published along with the draw results. Only those who submitted before that exact moment receive Invitations to Apply (ITAs); the rest will need to wait for the next round.
So, timing isn’t just important, it could be the deciding factor in your Canadian immigration journey
Real-Life Example of Tie-Breaking Rule in Express Entry
Let’s say two candidates, Rachel and Monica, both score 470 points in the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS) during an Express Entry draw. Without a tie breaking rule in Express Entry, it would be unclear who should receive an invitation to apply for permanent residence. However, thanks to the tie-breaking rule, the situation is easily resolved. If Rachel submitted their profile on January 1st at 10:00 AM and Monica submitted theirs on January 1st at 11:00 AM, the tie-breaking rule will prioritize Rachel due to their earlier submission time.
For example, during a draw, the tie-breaking rule might be applied with a cutoff time of January 1st, 2025, at 10:30 AM. This means any candidate with a CRS score of 470 or higher who submitted their profile before 10:30 AM would receive an invitation, while those who submitted after this time would not. This ensures that the selection process remains organized and candidates are chosen in a fair and transparent manner based on their entry time, preventing any disputes over who qualifies when scores are the same.
How to Increase Your CRS Score and Avoid the Tie-Breaking Rule in Express Entry
While the tie breaking rule in Express Entry ensures fairness, the best way to avoid relying on it is to improve your CRS score so you stand out clearly above the cut-off. The higher your score, the better your chances of receiving an invitation to apply (ITA) without being caught in a tie. There are several strategic ways to boost your score and move ahead in the rankings.
Consider improving the factors that affect the CRS score, which are;
- Age
- Education Level
- Proficiency in English or French
- Work Experience (both Canadian and foreign)
- Spouse or common-law partner factors
- Connections to Canada (such as having a sibling in Canada)
What can you do?
- First, consider improving your language test results, especially in English or French, as higher scores can significantly increase your CRS points.
- Gaining more work experience
- Completing a higher level of education or getting an Educational Credential Assessment (ECA) for foreign degrees can further raise your score.
- If you’re applying with a spouse, optimize your application by identifying who has the stronger profile.
Wrap up
At the end of the day, Express Entry is a competitive system, and every point counts. That’s why understanding the tie-breaking rule, knowing how your CRS score is calculated, and finding ways to improve it can make a real difference. Instead of relying on a technicality to get selected, it’s always better to focus on boosting your score and standing out in the pool.
Whether it’s retaking a language test, gaining more experience, or exploring options like a provincial nomination, every small effort adds up. And remember, the earlier you enter the pool with a strong profile, the better your chances of getting ahead of the tie.
Stay informed, stay prepared, and your Canadian dream could be closer than you think!